This web page was produced as an assignment for Genetics 677, an undergraduate course at UW‐Madison.
Chemical genetics
What is chemical genetics?
Chemical genetics is an approach to elucidating gene product function by directly testing for interactions of a protein with libraries of small molecules.
Molecules that bind to the protein of interest may provide insight into the functional mechanisms of that protein, which also has great utility for drug development [1].
In the case of ABCA1, using chemical genetics methods could help narrow down the parts of the protein that are essential for various parts of its overall function.
Molecules that bind to the protein of interest may provide insight into the functional mechanisms of that protein, which also has great utility for drug development [1].
In the case of ABCA1, using chemical genetics methods could help narrow down the parts of the protein that are essential for various parts of its overall function.
Small chemical inhibitor of ABCA1
I was unfortunately unable to find any chemical interaction partners for ABCA1 on ChemBank or PubChem, but a literature search turned up the compound glyburide [4]:
Glyburide
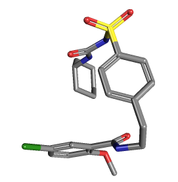
PubChem ID: CID 3488
Description: A sulfonylurea derivative
Use: Most often drescribed to type-II diabetics to help lower blood-glucose levels
Mechanism of inhibition: Believed to bind to and inhibit ATPase [4]
Description: A sulfonylurea derivative
Use: Most often drescribed to type-II diabetics to help lower blood-glucose levels
Mechanism of inhibition: Believed to bind to and inhibit ATPase [4]
Sources:
1. http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/genomics/poster_a2.html
2. http://chembank.broadinstitute.org/
3. http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4. Nieland T et al. Cross-inhibition of SR-BI- and ABCA1-mediated cholesterol transport by the small molecules BLT-4 and Glyburide. http://www.jlr.org/content/early/2004/04/21/jlr.M300358-JLR200.full.pdf
1. http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/genomics/poster_a2.html
2. http://chembank.broadinstitute.org/
3. http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4. Nieland T et al. Cross-inhibition of SR-BI- and ABCA1-mediated cholesterol transport by the small molecules BLT-4 and Glyburide. http://www.jlr.org/content/early/2004/04/21/jlr.M300358-JLR200.full.pdf