This web page was produced as an assignment for Genetics 677, an undergraduate course at UW‐Madison.
Homologous Genes
Most eukaryotic genes are conserved across species and perform similar biological functions.
This is the basic premise of performing experiments on model organisms to elucidate human gene function.
The relationships between genes can be ascertained by examining their similarity in DNA sequence, location in the genome and protein products.
Genes that derive from a common ancestor are referred to as "homologs".
This is the basic premise of performing experiments on model organisms to elucidate human gene function.
The relationships between genes can be ascertained by examining their similarity in DNA sequence, location in the genome and protein products.
Genes that derive from a common ancestor are referred to as "homologs".
Homologs on HomoloGene - NCBI's homology database
Some well-defined eukaryote homologs of the human ABCA1 gene (HomoloGene):
[1]
[1]
Gene phylogeny - Ensembl
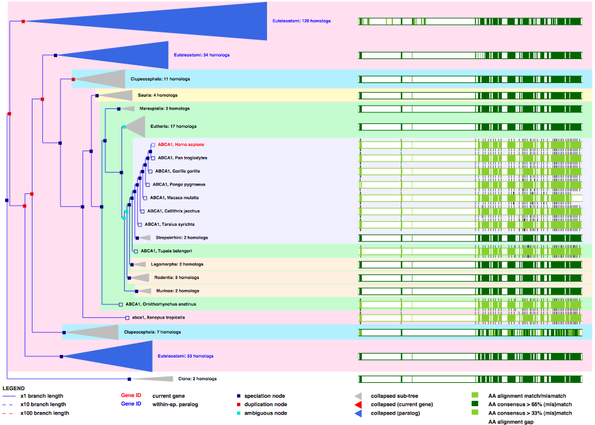
For full view and details about this image, see [2]
The large size of the ABCA1 gene was unfortunately incompatible with alignment and phylogeny generation tools available online.
However, the gene phylogeny at left shows the predicted phylogenetic relationship between the human ABCA1 gene and 277 genes in other species based on DNA and amino acid (AA) sequence homology (shown in green) [2].
Tangier disease model organism - Mus musculus
- Mouse Abca1 gene detail page
- Mouse/human gene ontology chart
Mouse homolog - Abca1
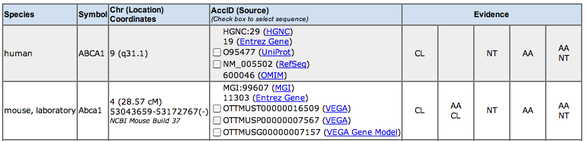
MGI mammalian orthology chart [3] Click the image for full view.
Evidence for homolgy
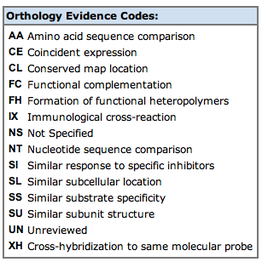
1. Conserved map location: The location of the mouse Abca1 gene in the mouse genome matches the location of the human ABCA1 gene in the human genome.
3. Amino acid sequence comparison: The ABCA1 and Abca1 proteins have similar amino acid sequences.
4. Nucleotide sequence comparison: The ABCA1 and Abca1 genes have similar nucleotide sequences.
Sources:
1. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore?Db=homologene&DbFrom=nuccore&Cmd=Link&LinkName=nuccore_homologene&IdsFromResult=189458805
2. http://www.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Gene/Compara_Tree?collapse=1794708%2C1794711%2C1794688%2C1794524%2C1794731%2C1794797%2C1794674%2C1794307%2C1794705%2C1794634%2C1794810%2C1794645%2C1794677;db=core;g=ENSG00000165029;r=9:107543283-107690518
3. http://www.informatics.jax.org/
1. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore?Db=homologene&DbFrom=nuccore&Cmd=Link&LinkName=nuccore_homologene&IdsFromResult=189458805
2. http://www.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Gene/Compara_Tree?collapse=1794708%2C1794711%2C1794688%2C1794524%2C1794731%2C1794797%2C1794674%2C1794307%2C1794705%2C1794634%2C1794810%2C1794645%2C1794677;db=core;g=ENSG00000165029;r=9:107543283-107690518
3. http://www.informatics.jax.org/

