This web page was produced as an assignment for Genetics 677, an undergraduate course at UW‐Madison.
Post-translational Modifications
Proteins must often undergo post-translational modifications before they can perform their biological functions. These can include the removal of some amino acids, or the addition of chemical groups to certain sites in the protein.
Post-translational modifications can greatly impact the ways in which a protein interacts with other proteins.
Post-translational modifications can greatly impact the ways in which a protein interacts with other proteins.
ABCA1 undergoes many post-translational modifications
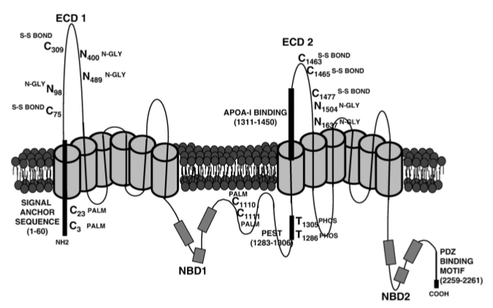
Post-translational modifications of ABCA1 [1]. Positions are given by nucleotide.
The mature ABCA1 protein is predicted to undergo several different types of post-translational modifications:
- Glycosylation: addition of a carbohydrate group that facilitates proper protein folding
- Disulfide bond formation: linkage between terminal sulfur atoms that facilitates protein folding
- Palmitoylation: Addition of a fatty acid group that facilitates association with cell membranes
- Phosphorylation: Addition of a polar phosphoryl group
Post-translational
modifications with
known functional
roles
- Phosphorylation on Ser-2054 regulates phospholipid efflux.
- Palmitoylation by DHHC8 is essential for membrane localization.
[2]
Palmitoylation is necessary for localization to
the cell membrane
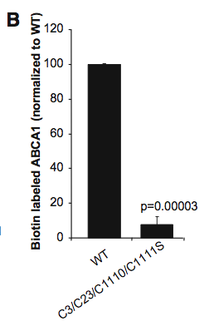
Figure 5 B from [3]
In cells that have mutations at amino acids that are normally palmitoylated (the right column in the graph at left), there is approximately 90% less ABCA1 detected at the plasma membrane compared to normal cells (right column).
This result indicates that palmitoylation of these residues is necessary for membrane localization, most likely for entering the membrane [3].
This result indicates that palmitoylation of these residues is necessary for membrane localization, most likely for entering the membrane [3].
Sources:
1. Kang MH, Singaraja R and Hayden MR. Adenosine-Triphosphate-Binding Cassette Transporter-1 Trafficking and Function. Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine. 2010; 20(2): 41-49.
2. http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O95477
3. Singaraja R, Kang MH, Vaid K, Sanders S, Vilas G, Arstikaitis P, Coutinho J, Drisdel R, El-Husseini A, Green W, Berthiaume L and Hayden M. Palmitoylation of ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter A1 Is Essential for Its Trafficking and Function. Cir Res. 2009; 105:138.
1. Kang MH, Singaraja R and Hayden MR. Adenosine-Triphosphate-Binding Cassette Transporter-1 Trafficking and Function. Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine. 2010; 20(2): 41-49.
2. http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O95477
3. Singaraja R, Kang MH, Vaid K, Sanders S, Vilas G, Arstikaitis P, Coutinho J, Drisdel R, El-Husseini A, Green W, Berthiaume L and Hayden M. Palmitoylation of ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter A1 Is Essential for Its Trafficking and Function. Cir Res. 2009; 105:138.
